What are some of the best supplements for longevity?
Which are the anti-aging supplements I take as a medical doctor and longevity hacker?
First, it’s important to differentiate between “longevity supplements” and “health supplements”:
Longevity supplements
Longevity supplements act on the aging process with the aim of slowing down aging and extending lifespan. These are substances like fisetin, microdosed lithium, alpha ketoglutarate (AKG), and so on (see further down).
Health supplements
Health supplements are vitamins, minerals and other micronutrients that in most cases unfortunately don’t extend maximum lifespan, but that can shorten lifespan and/or reduce quality of life if you are deficient in them. These are substances like vitamin D, potassium, vitamin A, B vitamins, and so on.
I explain the best health supplements here.
Longevity supplements versus health supplements
While many people have a significant interest in longevity supplements, health supplements are also important.
Health supplements contain micronutrients many people are deficient in, even if they eat “healthy”. Some important reasons for this are the following:
- Our bodies are not well made by nature to properly take up all micronutrients
- Many of our foods are very different now compared to thousands of years ago, or even 100 years ago, containing less micronutrients and/or being more unhealthy
- Nature (evolution) doesn’t care for us to have a long lifespan, so it has not perfected our body to absorb all needed micronutrients for a long, healthy life
- Our modern way of life exposes us to many stressors, requiring us to take in more micronutrients (stress and alcohol require more magnesium and B vitamins, sitting inside the whole day leads to vitamin D deficiency, etc).
- Many official recommended amounts of micronutrients are too low for optimal longevity, and are based on old or crude measurements and research
- Even when eating “healthily”, it’s very difficult to get all required micronutrients via food.
- When we get older, our body becomes less and less able to properly absorb nutrients (e.g. our skin is less able to produce vitamin D, our stomach and gut absorb less micronutrients, and so on).
In other words, you can take the best “longevity supplements”, but if you are still deficient in iodine or omega-3 fatty acids you still will shorten your lifespan and undermine long-term health.
In fact, a lifelong deficiency in just one micronutrient, like iodine, calcium or a specific B vitamin, could substantially undermine your health and increase your risk of many diseases.
So what are the best longevity and health supplements?
In this article, we will first concentrate on the best longevity (anti-aging) supplements. I discuss the most important health supplements on this page.
By writing “best” longevity supplements, I refer to substances that have the best and most convincing science and data behind them to slow down aging and extend lifespan.
These supplements are often a far cry away from many so-called “anti-aging” supplements that often are very popular but that don’t extend lifespan, or have very little or no science behind them. Some of these could even accelerate aging or increase mortality.
Put differently, you might be surprised that you don’t find many antioxidants or popular “anti-aging” vitamins or minerals in this longevity stack: most of these do not slow down aging or extend lifespan. This includes popular “anti-aging” substances like coenzyme Q10, ubiquinol, acetyl-cysteine (ACL), nicotinamide riboside (NR), and many others.
Despite that for some of these ingredients there are scientific studies showing they can indeed extend lifespan, there are many more studies showing they don’t extend lifespan, or even worse, can shorten lifespan. So I would be careful with these supplements.
Other anti-aging supplements I included may also surprise some, but in a positive way, like glucosamine or chondroitin, which are mainly used for joint health, but have been shown to slow aging and extend lifespan in many studies.
So, in no particular order, there are the following science-based anti-aging supplements:
LONGEVITY (ANTI-AGING) SUPPLEMENTS
1. Microdosed lithium
Lithium is a mineral found in rocks. From rocks, it seeps into water, eventually ending up in drinking water.
There are regions in the world where the drinking water is higher in lithium. Interestingly, scientists discovered that in these regions there is less mortality, less Alzheimer’s disease, less suicide, and even less crime (R,R,R,R,R,R,R).
This hinted to researchers that lithium, at low doses, could slow down aging, improve brain health and stabilize or improve mood, explaining why in regions with higher amounts of lithium in the drinking water there seems to be less suicide and crime.
Lithium has been shown to indeed extend lifespan and slow aging in various species (R,R,R,R,R,R).
In humans, lithium intake has been associated with reduced mortality (R,R,R), reduced risk of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s (R,R,R) and reduced suicide (R,R).
That lithium could reduce the risk of Alzheimer’s is very interesting. Currently, we have no drugs that can significantly impact the disease. Prevention is very important therefore. A study found that people who were exposed to lithium (red graph) had significantly less risk of Alzheimer’s disease and other kinds of dementia (R):
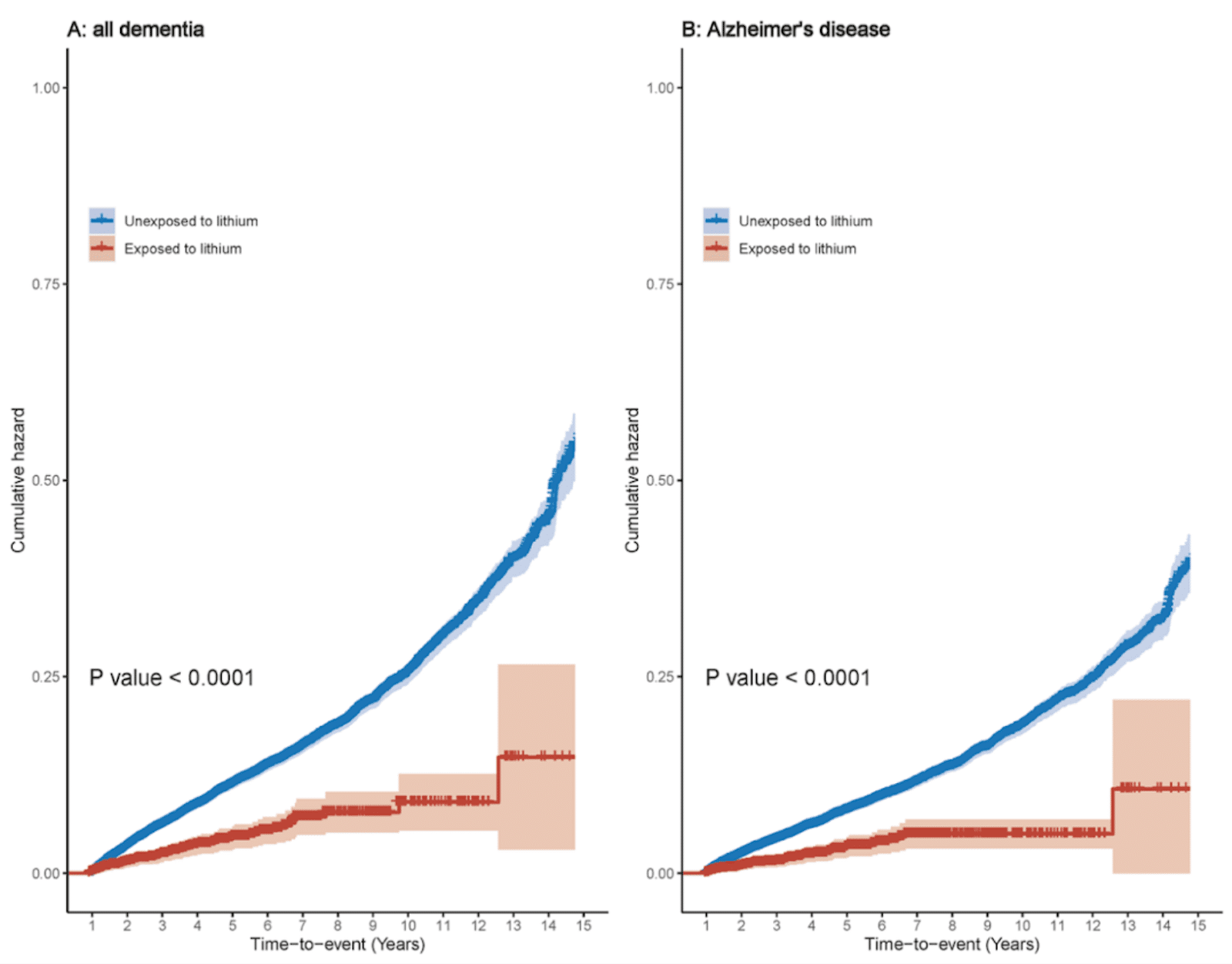
People exposed to lithium have a significantly reduced risk of dementia (red line) versus people have been unexposed to lithium (red line). Source: Association between lithium use and the incidence of dementia and its subtypes: A retrospective cohort study
Many of these studies involve people who took lithium as a drug, often because they have bipolar disorder (also called “manic-depressive disorder”).
Normally, people with bipolar disorder have a substantially increased risk of dementia.
However, that people with bipolar disorder who took lithium had actually less risk of dementia could indicate that lithium can significantly reduce the risk of dementia.
However, the doses of lithium given to bipolar patients are far higher compared to the doses of lithium one finds in drinking water, or “micro-dosed lithium”.
In psychiatric settings, doses of lithium are given that are hundreds of times higher compared to the micro-doses for longevity.
For example, to treat bipolar disorder, lithium is given in doses of a few hundred milligram of lithium per day, while in the context of longevity micro-dosed lithium is given, mostly in the range of 0.3 to 5 mg of pure lithium per day.
Despite the much lower doses of microdosed lithium, we see nonetheless that lithium in these dose ranges still has many beneficial effects for health and longevity.
And this especially for brain health. For example, clinical trials in humans in which participants took microdosed lithium showed improvements in Alzheimer’s diseases and mild-cognitive impairment (R,R,R), ideally when the trials last long enough (6 months or longer).
Lithium, longevity and aging
Lithium positively impacts many fundamental aging mechanisms.
For example, lithium has epigenetic effects, enabling the upregulation of genes that produce healthy proteins, like brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) (R,R).
Lithium also induces autophagy (R) which is the breakdown of proteins and other materials that would otherwise accumulate in the cells, an important process contributing to aging.
Does lithium cause kidney damage?
Some people worry that lithium can damage the kidneys.
After all, there have been many studies showing that lithium can damage the kidney.
However, this only when lithium is given in very high doses, in psychiatric settings. There, doses are given that are many hundreds of times higher than micro-dosed lithium for longevity purposes.
At such high doses, and when given chronically for years, lithium could indeed damage the kidneys. However, for micro-dosed lithium this is not the case: these low doses of lithium do not damage the kidneys.
In fact, we actually see that low doses of lithium can protect the kidneys against damage and aging (R,R).
According to Dr. Rujun Gong:
“Lithium may emerge as an effective anti-aging medication for the kidney and potentially other organ systems and help to better preserve the health and well-being of our aging population.”
– Dr. Gong, Division of Nephrology, Department of Medicine Center for Hypertension and Precision Medicine, University of Toledo College of Medicine, USA
In conclusion, low doses of lithium could actually protect the kidneys.
Example of high-quality supplement & dose
Optimal dose of lithium for longevity: 0.3 mg to 5 mg per day, taken in the morning, after breakfast.
Example of brand: link to Amazon.
2. Chondroitin sulfate
Chondroitin is an important component of cartilage, and of the extracellular matrix (ECM).
The extracellular matrix is a crucial substance in our body. It’s the viscous, sticky, gel-like matter in which all our cells are embedded and that functions as the glue that makes stick together our cells.
Without the ECM we would fall apart and be a big pile of individual cells.
The ECM consists of chondroitin, hyaluronic acid, collagen, elastin and other long, strand-like structures that give firmness to our tissues, including our skin and joints. This is also why chondroitin is often taken as a supplement to improve joint health.
However, most people don’t know that chondroitin also is a very interesting anti-aging supplement, which has been shown to activate various pro-longevity pathways, and to extend lifespan (R).
In humans, intake of chondroitin has been associated with reduced mortality (R). It’s one of the very few supplements that is associated with reduced risk of death and improved health.
It’s interesting to note that other molecules that are part of the extracellular matrix (ECM), like hyaluronic acid (which we will also discuss) and glucosamine, also extend lifespan in multiple species and have been associated with reduced mortality and aging-related diseases in humans (see further down).
In other words, these and other studies hint that extracellular matrix components could be interesting lifespan molecules.
In this regard, it’s not surprising that combining chondroitin with these ECM molecules could yield even better effects. For example, combining chondroitin with glucosamine has been associated with 65% reduction in cardiovascular mortality, and a 39% reduction in all-cause mortality in humans (R). Other studies also find reductions in mortality in humans who take chondroitin and glucosamine (R).
Chondroitin, longevity and aging
There are many ways in which chondroitin can slow aging and keep us healthier for longer.
For example, chondroitin has been shown to reduce inflammation. Chondroitin also can activate genes that encode components of the extracellular matrix. A strong extracellular matrix protects and maintains our cells better, including our stem cells.
Chondroitin can also mitigate atherosclerosis by improving the health of the cells that line the blood vessels (R). This can help to explain why studies show an association with chondroitin intake and significantly reduced risk of cardiovascular mortality in humans (R).
Besides the beneficial effect of chondroitin on lifespan, hearth health and other diseases, it can also improve skin health (R), which makes sense given chondroitin is an important component of the skin.
It’s important to take the chondroitin sulfate form, not the plain chondroitin form (e.g. chondroitin HCl or chondroitin KCl). The chondroitin sulfate is the same form that occurs in our body.
Ideally, one combines chondroitin sulfate with glucosamine sulfate (see further below) for maximum longevity benefits.
Longevity dose: 1200 mg per day (1000 to 1500 mg per day)
3. Glucosamine sulfate
Just like chondroitin, glucosamine sulfate is an important component of the extracellular matrix (ECM), the glue that embeds our cells, gluing them together. Glucosamine is an important component of our skin and joints.
Glucosamine is often promoted as a supplement to improve joint health. However, glucosamine is also a very interesting longevity substance.
Glucosamine and longevity
Glucosamine has been shown to extend lifespan in different organisms (R,R,R).
In humans, glucosamine was one of the very few supplements associated with reduced mortality (R,R).
People who take glucosamine also had less heart disease and cardiovascular mortality (R,R,R,R). A study published in the British Medical Journal (a very reputable medical journal) looked at the data of almost half a million people and found that glucosamine use was associated with 22% less cardiovascular death (R).
People who take glucosamine supplements have less risk of various cancers, such as colorectal cancer (R) and lung cancer (R), especially in combination with chondroitin.
Interestingly, one study found a large risk reduction from death from respiratory diseases (a 41% reduction) in people who take glucosamine (R). This could make sense, given lung tissue is a very elastic, flexible tissue which is very dependent on a proper extracellular matrix, which is composed of molecules like glucosamine (and chondroitin).
According to the conclusions of scientists who conducted a large glucosamine study, “regular glucosamine supplementation was associated with lower mortality due to all causes, cancer, CVD, respiratory and digestive diseases”.
It’s even better to combine glucosamine sulfate with chondroitin sulfate. Studies show that this combination can significantly reduce the risk of dying in humans.
Glucosamine, longevity and aging
Many studies in rodents show that glucosamine reduces inflammation (R), including the inflammation that happens in the blood vessel walls which contributes to atherosclerosis (R).
Glucosamine use in humans has been associated with lower proinflammatory proteins in the blood (such as C-reactive protein) (R,R).
Glucosamine also can improve blood vessel health (R). In humans, glucosamine improves the vascular endothelium, which are the cells that line our blood vessels (R).
Does glucosamine improve joint health?
A little word here about glucosamine supplements for joint problems, specifically osteoarthritis.
As we age, osteoarthritis becomes sooner or later a significant problem for almost everyone. Osteoarthritis is the wearing down of our joints, specifically the cartilage that lines our joints.
There exists lots of contradictory studies about glucosamine and joint health: some studies show that glucosamine can improve joint health, while others don’t show an effect.
Still today people, including doctors, claim that glucosamine supplements do not work to improve osteoarthritis.
To make a long story short, glucosamine very likely also improves joint health, least according to well-conducted studies.
The problem is that many studies done with glucosamine (and which don’t show an effect), have been done in a substandard way. For example:
- The studies often didn’t last long enough; like only a couple of months or even weeks. Mostly, damaged joints take a long time to heal.
- Many studies didn’t use high enough doses.
- Many studies used plain glucosamine (e.g. glucosamine HCL) instead of glucosamine sulfate (the latter form is preferred).
- Many studies use low-quality glucosamine (sulfate) supplements, or they use non-crystalline glucosamine sulfate supplements. High-quality, crystalline glucosamine reaches the joints in higher concentrations much better.
So it’s important to use high-quality, ideally more crystalline glucosamine sulfate supplements for a long enough time to get an effect.
In light of the innumerable animal and human studies showing beneficial effects of glucosamine on aging, improving many aging-related diseases and reducing mortality, it’s very likely that high-quality glucosamine in the right form and dose given long enough would also benefit our joints.
And as mentioned before, ideally glucosamine is combined with other important components of our joints and cartilage, namely chondroitin sulfate and hyaluronic acid, two extracellular matrix substances which also, not coincidentally, have been shown to extend lifespan and improve healthspan.
Ideal dose of glucosamine sulfate (not plain glucosamine): 1200 mg per day (1000 to 1500 mg per day).
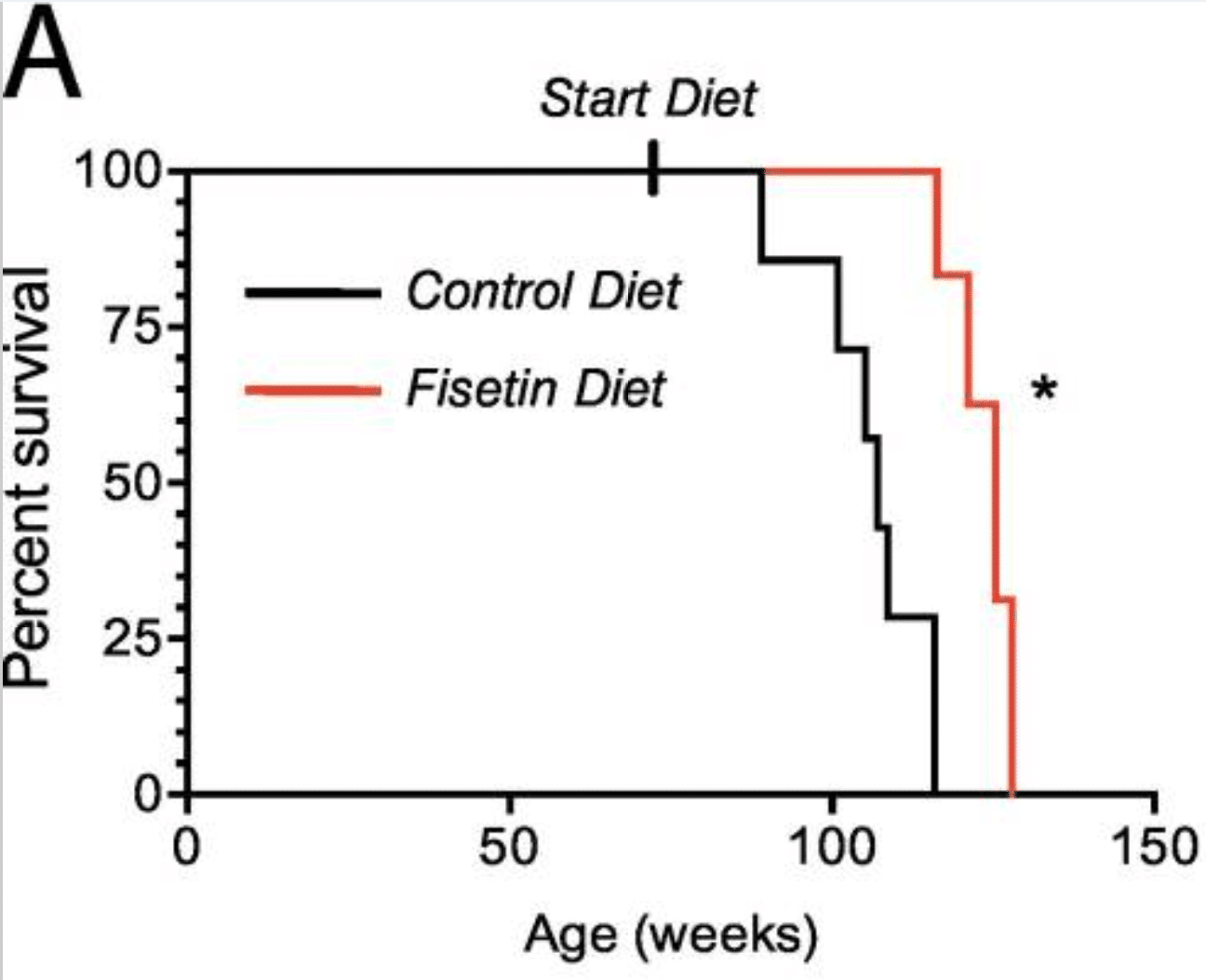
Old mice fed fisetin (started at 85 weeks of age, roughly equivalent to 75 years in humans) lived significantly longer (red line) compared to control mice (black line)
Fisetin also has been shown to improve various aging-related diseases, or to improve diseases that involve aging-related mechanisms such as protein accumulation (as in Hungtinton disease for example, in which a specific protein accumulates in the brain).
In a Hungtinton disease model, mice were given fisetin. While the control mice only lived on average for 104 days, the lifespan of the fisetin-fed mice was about 30% longer (139 days) (R).
Huntington’s disease is a deadly neurodegenerative disease in which a protein accumulates in the brain (huntingtin), leading to specific brain regions to die off. During aging, various other brain proteins accumulate (like beta amyloid, tau, TDP-43, and many others).
Is fisetin really a senolytic?
Often, fisetin is touted as a “senolytic” substance, implying it would be able to destroy senescent cells.
This could – perhaps- be the case when fisetin is given in very high doses, e.g. 1200 mg per day in humans during 3 days every month to “kill off” senescent cells.
However, at such high doses, it could be that fisetin (like quercetin) also damages healthy, normal cells, especially stem cells.
After all, many senolytics are “dirty senolytics”, meaning they do not only kill or damage senescent cells but can also kill or damage normal, healthy cells, including stem cells.
Interestingly, in mice lifespan studies, fisetin is given in relatively low doses. At lower doses, fisetin is likely not a senolytic. So it likely exerts its effects via other mechanisms than by being a senolytic.
For example, fisetin is a powerful inhibitor of inflammation (R,R). This is important, given that during aging low-grade inflammation starts to occur everywhere in our body (called “inflammaging”).
Fisetin could even have similarly strong anti-inflammatory activity as ibuprofen, a well-known anti-inflammatory drug (called “NSAID” or “Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug”) (R).
Fisetin also has epigenetic effects and can improve metabolism, for example by activating sirtuins (R,R).
Additionally, fisetin inhibits an important pro-aging pathway, namely the PI3/AKT-mTOR pathway (R,R). Inhibiting mTOR has been shown to extend lifespan in multiple species, as we will discuss later on.
Fisetin can also be an “indirect antioxidant”, meaning that it can induce transcription factors (like NRF2) that latch onto the DNA and upregulate the production of our own cellular antioxidant proteins, which is much better than taking direct antioxidants (like some vitamins and other “antioxidants”), which in most cases don’t extend lifespan.
In this regard, fisetin seems to be a special kid on the block regarding flavonoids. Flavonoids are found in healthy foods like fruits, vegetables and green tea for example, and are an important reason why these foods are healthy.
There exist many different flavonoids (e.g.flavonols, flavones, anthocyanidins, isoflavones, flavanones, flavan-3-ols, etc).
However, when looking at dozens of them, only two (fisetin and quercetin) were for example able to maintain glutathione (GSH) levels, which can combat oxidative stress.
Fisetin was also among the very few flavonoids shown to possess neurotrophic activity, for example by increasing the amount of neurites (these are projections from brain cells that make connections with other brain cells) (R).
Fisetin could also be beneficial for brain health and brain aging, for example by inhibiting the accumulation of beta amyloid protein, improving blood vessel health in the brain, and by reducing inflammation in the brain (neuroinflammation) (R,R,R,R,R).
In humans, we see that fisetin reduces inflammation (R) and improves the outcome of stroke (R). According to the researchers:
“Fisetin dramatically improved the treatment outcomes of the patients with stroke, as revealed by lower National Institute of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) scores. The beneficial effect of fisetin was likely attributable to reduced levels of MMP-2, MMP-9 [matrix metalloproteinases, which are proteins that break down the extracellular matrix], and CRP [a proinflammatory protein] in the serum, as evidenced by strong linear correlations between serum levels of such markers with the NIHSS scores in all enrolled patients.”
5. Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN)
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) is a precursor of a very important compound found in all our cells, namely NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide).
NAD+ is central for proper cellular functioning. It’s a relatively small molecule providing energy to innumerable proteins in our cells so they can carry out their function.
For example, NAD+ is needed for sirtuins and PARP proteins to repair our DNA and maintain our epigenome.
Unfortunately, during aging, levels of NAD+ in our cells decline (R,R).
Administering NMN increases levels of NAD+. Many studies show that NMN can improve various aspects of the aging process, such as:
- Improving blood vessel health (R,R,R,R,R).
- Improving stem cell health (R,R).
- Improving metabolism, including glucose intolerance, hepatic insulin sensitivity, lipid metabolism
- Restoring gene expression related to inflammation, oxidative stress and circadian rhythms (R).
- Improve fertility (R).
As you can see, NMN has many beneficial, anti-aging effects.
Let’s first go a bit deeper into the effects of NMN on fertility.
NMN and fertility
NMN has been shown to improve the health of egg cells (oocytes). That’s very interesting, because egg cells are in fact giant stem cells; once fertilized, just one egg cell keeps dividing until it has sprouted the 40,000 billions cells of which a human is composed.
NMN has shown to counteract various aging processes in egg cells, which could imply that NMN could also benefit stem cell health, which indeed seems to be shown by other studies demonstrating that NMN can improve stem cell function (R,R).
Interestingly, there are various case studies in which elderly women who have been in menopause for years, started to ovulate again after taking NMN.
Furthermore, specific companies have been using NMN and NMN analogues to rekindle fertility in old mares, or keep them fertile for longer.
Can NMN extend lifespan?
There are lots of studies showing that NMN can improve various aspects of aging or aging-related diseases in animals. But can it also extend their lifespan?
According to preliminary experiments done by professor David Sinclair, NMN can also extend lifespan in normal, healthy mice.
The words “normal and healthy” are important here, given that in many “longevity” studies diseased animals are used, e.g. animals that have deliberate mutations that cause a specific disease (like Alzheimer’s disease or a mitochondrial disease).
The way these animals age, or even have a specific disease, is often very different from how normal healthy animals age, or how humans have the specific disease in question.
Given NMN can extend lifespan of normal, healthy mice, and not of diseased, abnormal mice is very interesting.
However, even in the case NMN could not extend lifespan, it could very likely make old age a lot more fun. This by reducing or slowing down various aging-related diseases or mitigating aging-symptoms.
Let’s look at some effects of NMN in humans.
Effects of NMN in humans
In humans, NMN has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity in pre-diabetic women (R). This is a good thing, given that during aging, insulin resistance increases, which in turn increases the risk of various aging-related diseases such as heart disease and Alzheimer’s disease, and of aging itself.
NMN also enhanced muscular health in elderly men (R). During aging, muscle health and strength diminishes, which leads to reduced mobility, an increased risk of falls and many other problems.
NMN can also increase endurance in humans, providing more energy and stamina (R).
Can NMN be taken orally (by mouth)?
It’s important to note that in the human studies we just discussed, NMN is taken via mouth (orally), so not injected intravenously or taken sublingually ( dissolved under the tongue).
It also involves normal, plain NMN powder (not liposomal NMN), and is given in most studies in doses of around 250 mg of NMN per day.
I mention this because some people believe that NMN should be taken singlingually or even intravenously, which is not the case.
Lots of people also think that NMN should be taken in liposomal form – which means it would need to be encapsulated in tiny fat droplets to improve its absorption. This is all not necessary. Orally taken, non-liposomal NMN works fine, as these studies demonstrate.
For people still doubting, one of the most renowned specialists in NMN, Harvard Professor David Sinclair, takes normal, non-liposomal NMN during breakfast (so orally, not sublingually).
Professor Sinclair however takes a high dose of NMN – around 1000 mg per day. But such a high dose is not necessarily needed. We see that in most human studies around 250 mg of NMN per day already has beneficial effects (R,R,R).
Nonetheless, it could be that higher doses could be even more beneficial; especially as one gets older.
Therefore, one recommendation is taking around 250 to 500 mg for people in their thirties and forties, and around 600 mg to 750 mg per day for people in their fifties and sixties, and 750 mg to 1000 mg per day for 70-plus people.
However, one should be mindful not to take too much NMN. We see that likely from doses of more than 2000 mg per day the beneficial effects of NMN are actually reduced.
It’s also advised to take NMN in the morning, because NMN taken at noon or in the evening, can give some people too much energy in the sense it hinders them from falling asleep at night.
6. Alpha-ketoglutarate (AKG), the calcium form
Alpha-ketoglutarate (AKG) is a substance found in every cell in our body. It’s actually an important fuel for our mitochondria, the power plants of our cells.
Studies show that alpha-ketoglutarate extends lifespan in multiple species.
In humans, alpha-ketoglutarate can protect organs during physiological stress, as during operations (R,R,R,R,R,R) or dialysis (R,R,R,R).
Alpha-ketoglutarate also plays a role in collagen synthesis and bone health. It could also slow down osteoporosis in humans (R,R).
In some preliminary human studies, alpha-ketoglutarate could rejuvenate humans, measured via epigenetic clocks (R).
Alpha-ketoglutarate, longevity and aging
Alpha-ketoglutarate is involved in the production of energy. To be more precise, alpha-ketoglutarate is a metabolite of the Krebs cycle, which is the chemical process in the mitochondria that creates most of the energy for our cells.
But AKG has many other functions in the body.
For example, AKG is involved in epigenetic regulation. The epigenome determines which genes are activated or not. A decline in epigenetic function plays an important role in aging, as we explained in the chapter about the causes of aging.
Alpha-ketoglutarate plays an important role in organizing and maintaining the epigenome, given TET enzymes need alpha-ketoglutarate to function properly. TET enzymes are important regulators of the epigenome; they remove methyl groups from DNA. To do this, they need alpha-ketoglutarate. And vitamin C. So in this regard, vitamin C works synergistically with alpha-ketoglutarate.
That’s why vitamin C also has epigenetic effects, and is also an important substance for optimal longevity, as I’ll explain later.
Best form of alpha-ketoglutarate
It’s important to take the calcium form alpha-ketoglutarate, namely “calcium alpha-ketoglutarate”, instead of the regular “alpha-ketoglutarate” (as most supplements contain).
It’s the calcium AKG form that has been used in scientific experiments demonstrating lifespan extension.
Scientists believe that the calcium atom in the calcium alpha-ketoglutarate compound stabilizes the alpha-ketoglutarate, and also slows down its absorption, prolonging its effect.
I take 2,000 mg of calcium alpha-ketoglutarate per day.
7. Glycine
Glycine is a small amino acid that occurs naturally in our body.
Glycine has been shown to extend lifespan in multiple species (R,R,R,R,R).
Studies in humans show that if you give glycine to people, it can reduce inflammation (R,R) , enhance glucose metabolism (R,R,R,R) and improve aspects of aging (R), including degenerative diseases like osteoarthritis and osteoporosis (R).
Higher levels of glycine have been associated with a reduced risk of a heart attack in humans (R) and a healthier metabolism (R,R,R,R).
Glycine could also help protect the brain against stroke damage (R), and could improve memory (R).
Glycine also has a calming, relaxing effect. Therefore it’s best to take it before sleep.
Longevity dose for glycine: 2,000 mg per day
8. Hyaluronic acid
Hyaluronic acid is an important substance for our skin and joints.
In fact, hyaluronic acid is found everywhere in the body given that it’s an important component of the glue that makes our cells stick together.
Hyaluronic acid is part of the extracellular matrix (ECM), which surrounds our cells and glues cells together. Without an extracellular matrix, we would be a pile of cells lying on the floor.
Hyaluronic acid has been shown to have interesting lifespan effects. Components of hyaluronic acid like acetyl-glucosamine have been shown to extend lifespan in animals (R). Hyaluronic acid on itself also can extend lifespan (R).
Interestingly, one of the reasons why naked mole rats live much longer than normal rats, is due to the fact they produce more and stronger hyaluronic acid. More specifically, they produce hyaluronic acid with a higher molecular mass (R). This kind of hyaluronic acid protects their cells better, and also reduces the risk of cancer cells metastasizing (spreading) because thicker hyaluronic acid means it’s more difficult for cancer cells to penetrate tissues.
Increasing enzymes that make hyaluronic acid also increases lifespan in mice (R).
Does oral hyaluronic acid reduce wrinkles and joint problems?
Most people will know hyaluronic acid as an ingredient in skin creams or serums to reduce wrinkles (as I also discuss in the article about best anti-aging skin products). Given hyaluronic acid is very good at attracting water, it can make our skin more moisturized, making it look less dried-out, and thus younger.
However, when taken orally, hyaluronic acid can also reduce wrinkles – in a better and more fundamental way then via skin creams.
The reason for this is that when taken orally, hyaluronic acid is broken down into smaller components in the gut. These parts are then taken up from the gut into the bloodstream (R,R), reaching our skin cells and nudging them to produce more hyaluronic acid, leading to reduced wrinkles and a younger-looking skin (R,R,R,R).
Given hyaluronic acid is also part of the cartilage and ligaments forming our joints, it can also improve osteoarthritis of our joints, like in the knee (R,R,R).
There are different forms of hyaluronic acid. A good manufacturer of hyaluronic acid is Hyabest (this form of hyaluronic acid has been tested clinically in various studies, demonstrating improvements in skin appearance).
Dose I take: 120 mg of hyaluronic acid before bed.
HEALTH SUPPLEMENTS (VS LONGEVITY SUPPLEMENTS)
We just discussed the best anti-aging, longevity supplements.
However, it’s important to also take health supplements. These are vitamins, minerals and other micronutrients many people are deficient in, like vitamin D, magnesium or iodine, even when people eat healthy.
So you can take the best longevity supplements, but if you are deficient in important health supplements this can also undermine your longevity and shorten lifespan.
We discuss the most important health supplements on this page.